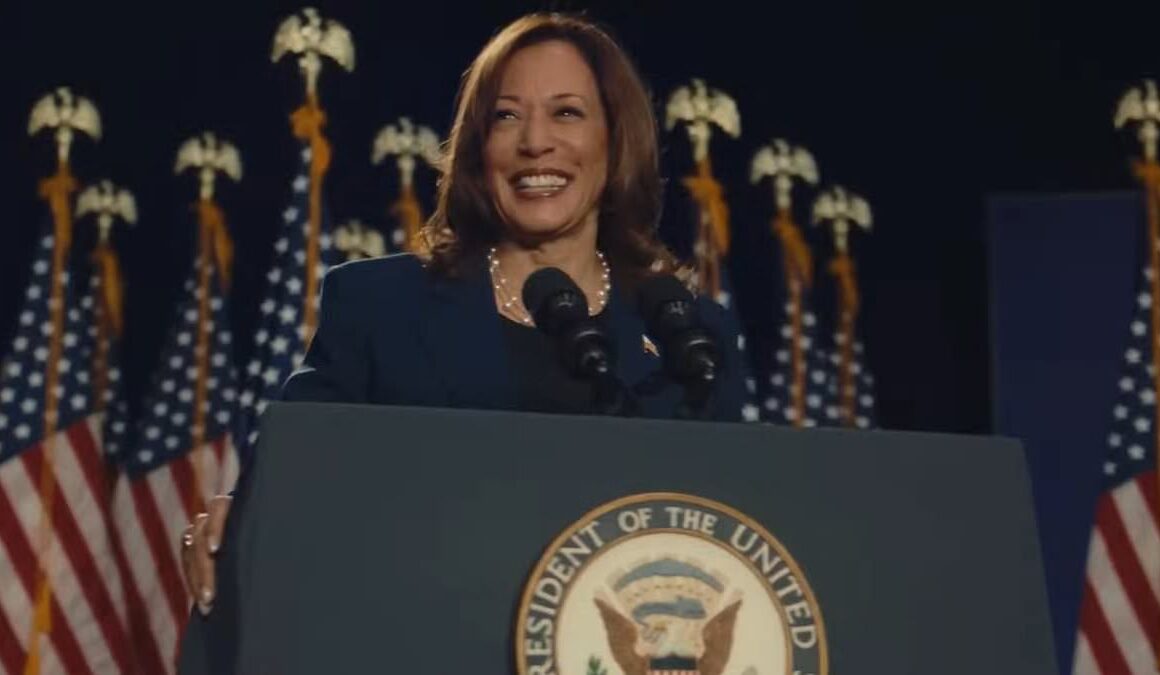
Controversial billionaire Elon Musk is being accused of breaking his platform’s rule on deepfakes after he posted a doctored video mocking Vice President Kamala Harris with manipulated voice.
The clip has been viewed nearly 130 million times by X users. In the clip, the fake Harris’ voice says: ‘I was selected because I am the ultimate diversity hire.’ It then adds that anyone who criticizes her is ‘both sexist and racist.’
The world’s richest man captioned the video: ‘This is amazing.’ It was originally posted by the X account @MrReaganUSA, a designated parody account that posts pro-Donald Trump content.
The video goes on to refer to Harris, 59, as a ‘deep state puppet.’ The clip was edited from an actual campaign video that the former California senator released last week.
Musk, who has endorsed Donald Trump and embraced many alt-right talking points in recent months, failed to acknowledge the video was satire in his original posting.
Among those who commented on Musk’s video was Veep creator Armando Iannucci who labeled the South African a ‘gullible tech-puppet.’

Elon Musk has mocked those who have been critical of him posting the video, claiming it’s ‘satire’

Vice President Kamala Harris’ campaign are on the defensive, calling both Musk and Donald Trump out for spreading lies
Meanwhile California Governor Gavin Newsom who about the video remarking: ‘Manipulating a voice in an “ad” like this one should be illegal. I’ll be signing a bill in a matter of weeks to make sure it is.’
Musk, 53, responded to Newsom, who was rumored to have been mulling a presidential run in 2024: ‘I checked with renowned world authority, Professor Suggon Deeznutz, and he said parody is legal in America.’
According to X’s guidelines on the subject, users may not share ‘synthetic, manipulated, or out-of-context media that may deceive or confuse people and lead to harm.’
Clips of satire are excluded as long as they do not ’cause significant confusion about the authenticity of the media.’
The video uses many of the same visuals as a real ad that Harris released last week launching her campaign. But the video swaps out the voice-over audio with another voice that convincingly impersonates Harris.
‘I, Kamala Harris, am your Democrat candidate for president because Joe Biden finally exposed his senility at the debate,’ the voice says in the video.
It claims Harris is a ‘diversity hire’ because she is a woman and a person of color, and it says she doesn’t know ‘the first thing about running the country.’
The video retains ‘Harris for President’ branding. It also adds in some authentic past clips of Harris.

An image of Vice President Harris from her ‘We Choose Freedom’ campaign video

The video features Harris talking about reproductive freedom. Abortion has been a top issue for the vice president on the campaign trail since the Supreme Court overturned Roe v Wade
Mia Ehrenberg, a Harris campaign spokesperson, said in an email to The Associated Press: ‘We believe the American people want the real freedom, opportunity and security Vice President Harris is offering; not the fake, manipulated lies of Elon Musk and Donald Trump.’
The widely shared video is an example of how lifelike AI-generated images, videos or audio clips have been utilized both to poke fun and to mislead about politics as the United States draws closer to the presidential election.
It exposes how, as high-quality AI tools have become far more accessible, there remains a lack of significant federal action so far to regulate their use, leaving rules guiding AI in politics largely to states and social media platforms.
The video also raises questions about how to best handle content that blurs the lines of what is considered an appropriate use of AI, particularly if it falls into the category of satire.
X users who are familiar with the platform may know to click through Musk’s post to the original user’s post, where the disclosure is visible. Musk’s caption does not direct them to do so.
While some participants in X’s ‘community note’ feature to add context to posts have suggested labeling Musk’s post, no such label had been added to it as of Sunday afternoon.
Two experts who specialize in AI-generated media reviewed the fake ad’s audio and confirmed that much of it was generated using AI technology.

Musk has long been supportive of Donald Trump’s presidential campaign and other alt-right causes
One of them, University of California, Berkeley, digital forensics expert Hany Farid, said the video shows the power of generative AI and deepfakes.
‘The AI-generated voice is very good,’ he said in an email. ‘Even though most people won’t believe it is VP Harris’ voice, the video is that much more powerful when the words are in her voice.’
He said generative AI companies that make voice-cloning tools and other AI tools available to the public should do better to ensure their services are not used in ways that could harm people or democracy.
Rob Weissman, co-president of the advocacy group Public Citizen, disagreed with Farid, saying he thought many people would be fooled by the video.
‘I don’t think that’s obviously a joke,’ Weissman said in an interview. ‘I’m certain that most people looking at it don’t assume it’s a joke. The quality isn’t great, but it’s good enough. And precisely because it feeds into preexisting themes that have circulated around her, most people will believe it to be real.’
Weissman, whose organization has advocated for Congress, federal agencies and states to regulate generative AI, said the video is ‘the kind of thing that we’ve been warning about.’
Other generative AI deepfakes in both the U.S. and elsewhere would have tried to influence voters with misinformation, humor or both.
In Slovakia in 2023, fake audio clips impersonated a candidate discussing plans to rig an election and raise the price of beer days before the vote.
In Louisiana in 2022, a political action committee’s satirical ad superimposed a Louisiana mayoral candidate’s face onto an actor portraying him as an underachieving high school student.
Congress has yet to pass legislation on AI in politics, and federal agencies have only taken limited steps, leaving most existing U.S. regulation to the states.
More than one-third of states have created their own laws regulating the use of AI in campaigns and elections, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures.
Beyond X, other social media companies also have created policies regarding synthetic and manipulated media shared on their platforms.
Users on the video platform YouTube, for example, must reveal whether they have used generative artificial intelligence to create videos or face suspension.